Logs
The Logs section consists of three primary log types designed to provide complete visibility into user interactions, automation processes, and search activities within your platform.
Queries Logs
Purpose:
The Queries Logs store detailed records of all interactions between users and the AI module, including both text-based requests and image-generation requests.
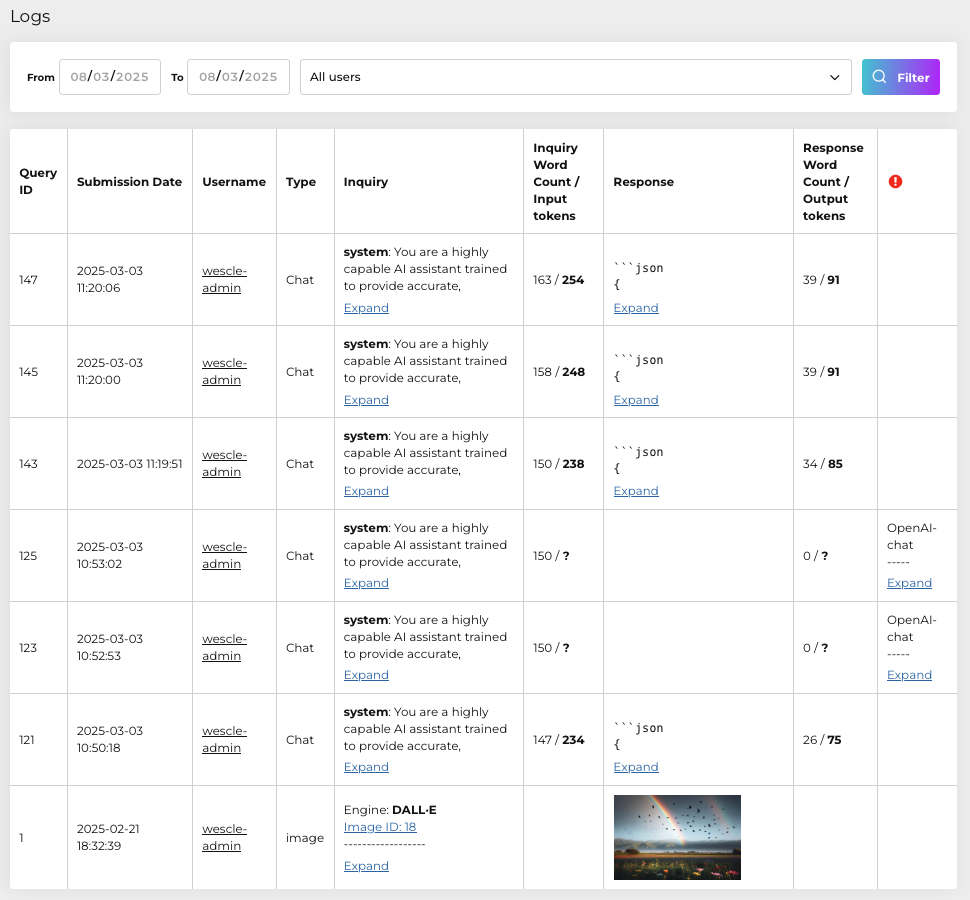
Details Provided:
• Query ID: Unique identifier for each query.
• Submission Date: Exact timestamp of the query.
• Username: Identifies the user who made the request.
• Type: Indicates whether the query was text-based (“Chat”) or an image generation (“Image”).
• Inquiry: The actual content of the user’s request, with an option to expand to see full details.
• Inquiry Word Count / Input Tokens: Shows the length of each request, crucial for analyzing usage patterns and costs.
• Response: The exact response generated by the AI, expandable for detailed inspection.
• Response Word Count / Output Tokens: Indicates the length of the AI’s response, helpful for tracking resource utilization.
Automation Logs
Purpose:
Automation Logs track and document all automated tasks processed by the Automation Module. This provides complete transparency for monitoring, troubleshooting, and refining automated processes.
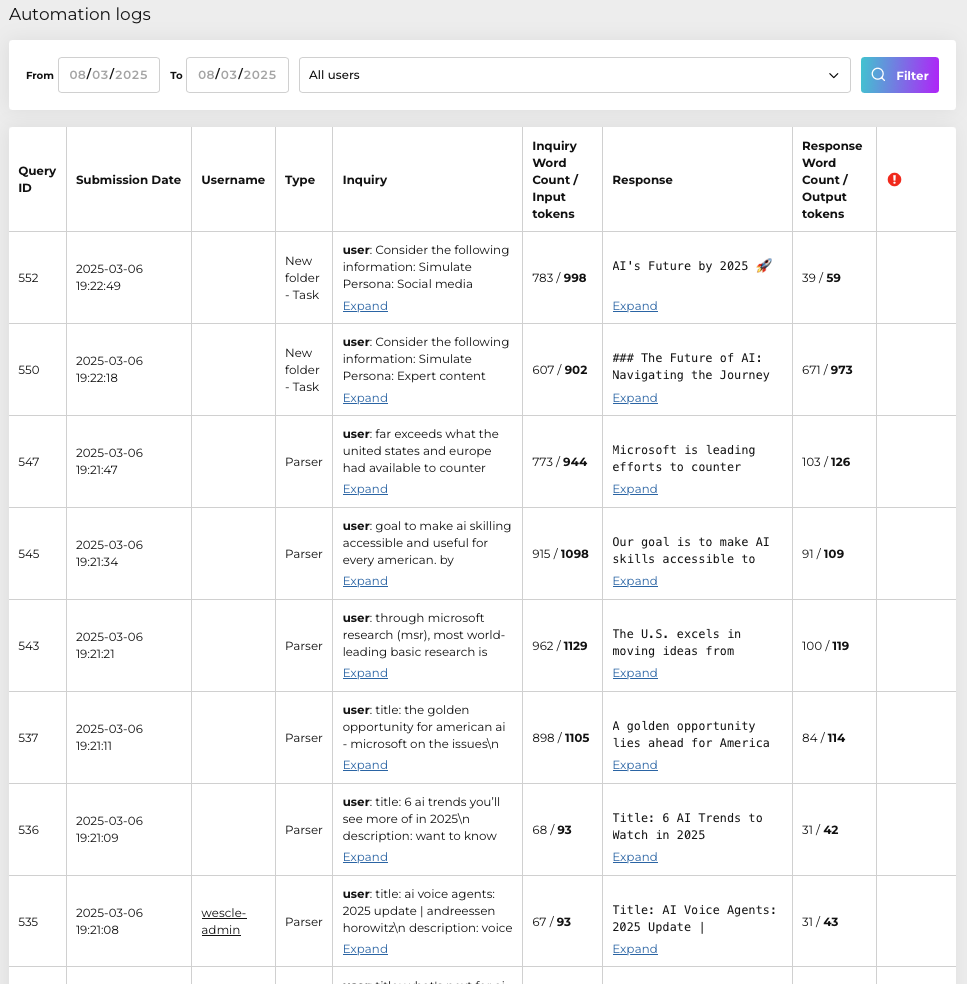
Details Provided:
• Query ID: Unique identifier for each automation task.
• Submission Date: Timestamp of the automation event.
• Username: User associated with the automation trigger.
• Type: Clearly indicates the type of automation (e.g., Parser, Task).
• Inquiry: The input or action requested from the automation system, with expandability for complete visibility.
• Inquiry Word Count / Input Tokens: Measures the complexity and resource usage of each automated request.
• Response: Outcome or result generated by the automation, fully expandable for review.
• Response Word Count / Output Tokens: Length of the automation’s response, essential for resource tracking and analytics.
Search Logs
Purpose:
Search Logs capture every search activity made by users on your website, enabling in-depth analysis of user behavior and preferences, and aiding in content optimization and enhancement of AI-driven responses.
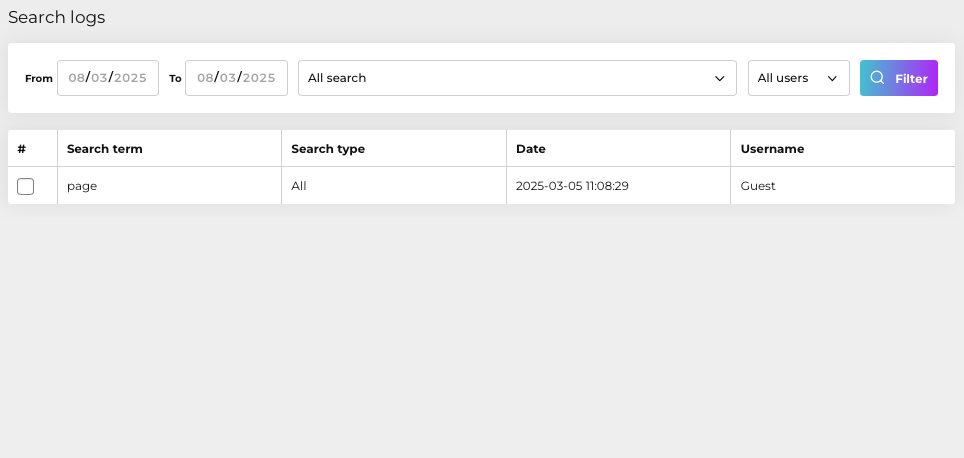
Details Provided:
• Search Term: Keywords or phrases entered by users.
• Search Type: Category or method of search (e.g., all content, specific sections).
• Date: Timestamp when the search was conducted.
• Username: Identity of the user performing the search (can also appear as “Guest”).
Filtering and Analysis
All log types support advanced filtering options:
• Date Range: Narrow down logs by specific dates.
• User-based filtering: View logs from specific users or groups.
• Type-based filtering: Quickly isolate logs by interaction type.
These logs collectively offer powerful tools to understand and optimize interactions, automate processes effectively, and precisely identify user interests, ultimately improving the user experience and system performance.